
“Do snakes give birth through their mouth?” This intriguing question often leads to myths and misconceptions about snake reproduction.
In this article, we will debunk this common misunderstanding and explore the fascinating world of snake reproduction.
You will learn about the different methods of snake reproduction, including oviparous and viviparous snakes, their unique adaptations for survival, and the behaviors that lead to this misconception.
By the end, you will gain a deeper understanding of how snakes bring new life into the world and dispel any misconceptions about snakes giving birth through their mouths.
Table of Contents
Answer To Do Snakes Give Birth Orally?
No, snakes do not give birth orally. The idea that snakes give birth through their mouths is a myth. Snakes have their unique reproductive methods, which involve either laying eggs (oviparous) or giving live birth (viviparous). In both cases, the birth process occurs through the cloaca, a single opening used for both reproduction and waste elimination.
While some snake species may carry their young in their mouths for protection and transportation, this behavior is not related to the actual birthing process.
Snakes give birth through their cloaca, and the mouth is not involved in the birthing process.
Snakes’ Reproductive Methods
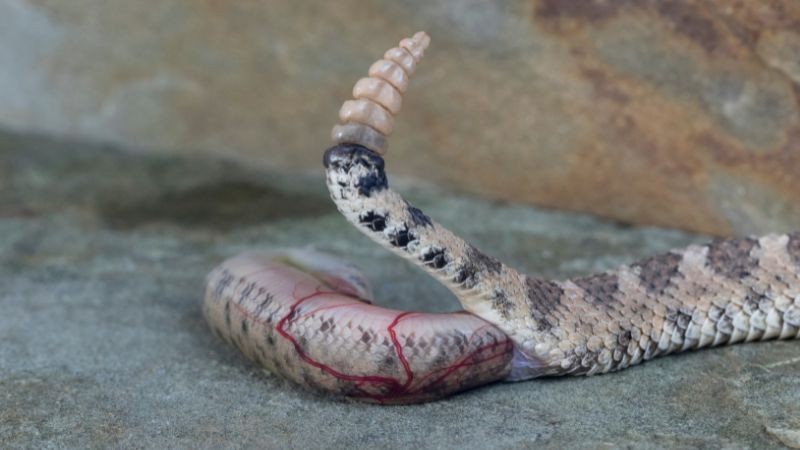

Snakes are fascinating creatures with diverse reproductive methods. Unlike mammals, snakes don’t give birth to live young as a general rule, but there’s more to their reproductive story than meets the eye.
Let’s dive into the intriguing world of snake reproduction and uncover the truth about whether they give birth through their mouths.
Overview of Different Snake Reproduction Methods
When it comes to bringing new life into the world, snakes have a few tricks up their scales. There are three main methods of snake reproduction: oviparous, viviparous, and a combination of both.
Oviparous snakes lay eggs, which hatch into baby snakes after an incubation period. These eggs are usually laid in a safe and warm spot to ensure the survival of the offspring.
Viviparous snakes, on the other hand, give live birth, similar to mammals.
They retain the eggs inside their bodies until the embryos are fully developed, and then the young snakes are born alive.
Oviparous Snakes
Oviparous snakes are egg-layers, and this method of reproduction is more common among snake species. Female oviparous snakes produce eggs within their bodies, and once the eggs are fully formed, they are laid in a suitable environment.
This can be a hole in the ground, decaying vegetation, or even inside termite mounds, depending on the snake species.
The female carefully selects a safe location for her eggs, often away from potential predators. Once the eggs are deposited, the female leaves them to develop independently.
The eggs are equipped with everything the young snakes need to survive, including a protective shell and nutrients.
Viviparous Snakes
Viviparous snakes take a more nurturing approach to reproduction. These snakes retain the eggs inside their bodies until the embryos are fully developed.
The developing snakes receive nourishment from the mother through a placenta-like structure, similar to mammals.
Once the gestation period is complete, the mother gives birth to live baby snakes.
This method allows the mother to provide more protection and care for her offspring, which can be especially advantageous in harsh environments or situations where predators are abundant.
Misconception About Snakes Giving Birth Through Their Mouths
There’s a persistent myth that some snakes give birth through their mouths. While snakes have a unique way of ingesting their prey through their mouths, they certainly don’t use this orifice for birthing.
The confusion might arise from the fact that snakes can open their mouths widely to accommodate large prey.
Snakes give birth through their cloaca, a single opening used for both reproduction and waste elimination.
The cloaca is located on the underside of the snake’s body, and it serves as the exit point for both the baby snakes and waste materials.
In conclusion, snakes have a remarkable array of reproductive methods, each suited to their specific environment and lifestyle.
From the egg-laying oviparous snakes to the live-bearing viviparous ones, these unique creatures continue to captivate and surprise us with their incredible adaptations for survival.
Snake Reproduction Myths
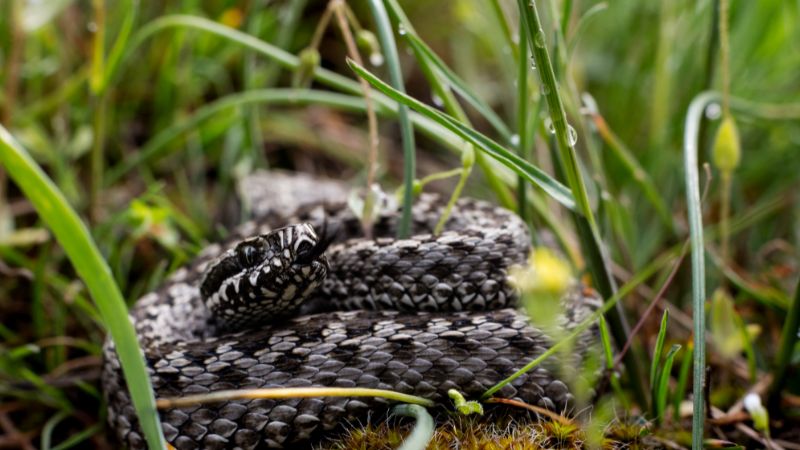

Snakes have always intrigued and, at times, frightened humans, leading to the creation of various myths and misconceptions about these enigmatic creatures.
One prevalent myth surrounding snake reproduction is the notion that snakes give birth through their mouths. Let’s debunk this misconception, explore its origin, and clarify the role of a snake carrying babies in its mouth.
Possible Origins of the Myth
Like many myths, the origin of the belief that snakes give birth through their mouths is shrouded in mystery.
It’s possible that ancient cultures observing snakes carrying their young in their mouths misconstrued this behavior as the actual birthing process.
The imagery of a snake with its mouth full of wriggling hatchlings might have been misinterpreted as the snake giving birth through its oral cavity.
Additionally, the serpentine symbolism found in numerous cultures and mythologies throughout history might have contributed to the creation of this misconception.
Snakes are often associated with birth, death, and renewal due to their ability to shed their skin, making them powerful symbols in folklore and religious beliefs.
Oviparous Snakes
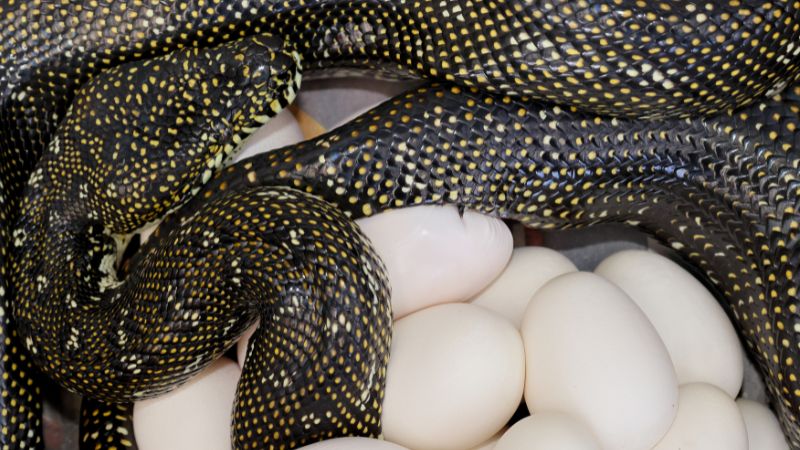

The Process of Egg-Laying in Snakes
Oviparous snakes, the egg-layers among the serpentine community, have a fascinating process of reproducing through the creation and deposition of eggs.
Female oviparous snakes develop eggs within their bodies, which are then laid in carefully chosen locations.
The eggs are equipped with everything necessary for the survival of the developing snakes, making this method of reproduction highly efficient.
Different Species of Oviparous Snakes
Numerous snake species fall under the category of oviparous.
Some of the most well-known oviparous snakes include the common garter snake (Thamnophis sirtalis), the ball python (Python regius), and the corn snake (Pantherophis guttatus).
Each species has its unique characteristics, from the color patterns to the habitats they prefer.
Insight into the Incubation Period and Hatching Process
After laying the eggs, the female oviparous snake leaves them to develop independently. The incubation period varies depending on factors such as temperature and humidity.
During this time, the developing snakes receive nourishment from the yolk sac, which is a vital source of nutrients for their growth.
Once the incubation period concludes, it’s time for the eggs to hatch. The baby snakes use a specialized tooth called an egg tooth to break through the shell.
This temporary tooth falls off shortly after hatching. Once free from the confines of their eggs, the young snakes embark on their journey to explore the world around them.
Viviparous Snakes
Explanation of Live Birth in Snakes
Viviparous snakes have a unique way of bringing their offspring into the world – live birth. Instead of laying eggs, the female retains the developing embryos within her body until they are ready to be born.
This method allows for more direct maternal care, enhancing the survival chances of the newborn snakes.
Examples of Viviparous Snake Species
Among the viviparous snakes, we encounter fascinating species such as the garter snake (Thamnophis sirtalis), the boa constrictor (Boa constrictor), and the copperhead snake (Agkistrodon contortrix).
Each species has distinct adaptations that aid in their survival in diverse environments.
The Gestation Period and Birth Process
The gestation period for viviparous snakes varies depending on factors like species, climate, and the availability of food.
During this time, the mother nourishes her developing offspring through a placenta-like structure, ensuring they receive essential nutrients for their growth.
When the gestation period concludes, the mother snake gives birth to live young. The birth process can be a remarkable event, with tiny snakes emerging from their mother’s body.
The newborn snakes are immediately capable of fending for themselves, but some species may receive additional protection and guidance from their mother during their early days.
In conclusion, snakes exhibit a wide array of reproductive methods, each tailored to suit their respective environments and lifestyles.
Oviparous snakes lay eggs and leave them to develop independently, while viviparous snakes give birth to live young and provide more direct maternal care.
Understanding these distinctive processes enhances our appreciation for these captivating creatures and their incredible adaptations for survival.
Snake Reproduction Adaptations
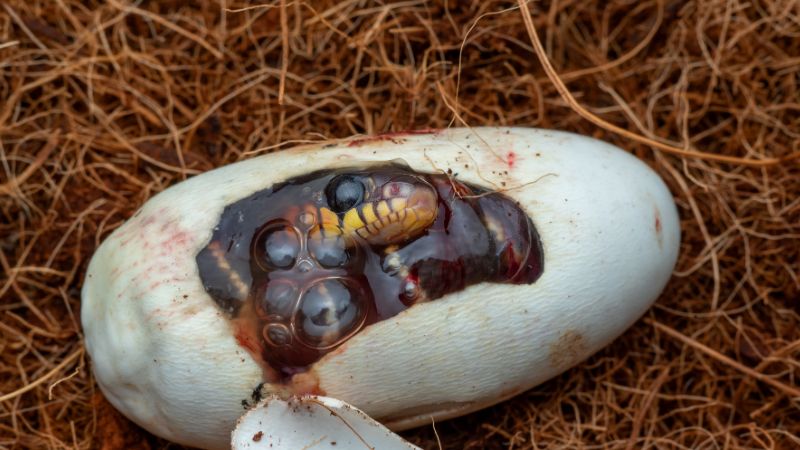
Unique Adaptations for Reproduction in Snakes
Snakes have evolved a variety of remarkable adaptations to ensure successful reproduction. From their reproductive anatomy to behavior, these adaptations are finely tuned to suit their environments and maximize the chances of offspring survival.
Understanding these adaptations provides valuable insights into the fascinating world of snake reproduction.
Reproductive Strategies for Survival and Offspring Protection
Survival is the primary driving force behind the diverse reproductive strategies of snakes. Some snake species employ camouflage to protect their eggs, laying them in environments that blend seamlessly with their surroundings.
Others may lay their eggs in clusters to enhance the chances of survival through strength in numbers.
Certain species have developed unique behaviors to protect their offspring. For example, some mother snakes, like the green anaconda (Eunectes murinus), guard their nests fiercely, ensuring predators are kept at bay during the incubation period.
Such strategies significantly improve the chances of the baby snakes reaching maturity.
Exploration of Parental Care in Snakes
While snakes are not known for extensive parental care, some species do exhibit surprising nurturing behaviors.
In viviparous snakes, maternal care often involves the mother protecting and guiding her young during their early days. This protection may extend to finding suitable hiding spots and teaching them to hunt for prey.
In a few species, parental care goes beyond just protecting the offspring. Some female snakes will stay with their young for extended periods, ensuring they learn essential survival skills.
This rare form of parental care exemplifies the dedication of these reptiles to ensuring the success of the next generation.
Other Fascinating Snake Reproduction Facts
Beyond their reproductive methods and behaviors, snake reproduction offers a trove of intriguing facts.
For instance, some snake species can store sperm for extended periods, allowing them to fertilize eggs at a later time. This adaptation enables snakes to reproduce even when suitable mates may not be readily available.
Uncommon Reproductive Behaviors in Certain Snake Species
Certain snake species showcase particularly unique reproductive behaviors. For instance, the female red-sided garter snake (Thamnophis sirtalis parietalis) congregates with numerous males in massive mating balls, resulting in a phenomenon known as “mating frenzy.”
This mass gathering ensures successful fertilization and genetic diversity.
Moreover, the female African egg-eating snake (Dasypeltis) has a fascinating method of reproducing.
As the name suggests, this snake consumes bird eggs, but it does not lay eggs of its own. Instead, it develops its embryos inside its body and gives birth to live young, despite being classified as an oviparous species.
In conclusion, snake reproduction is a captivating topic that delves into the complex and diverse strategies these reptiles employ to ensure the survival of their species.
From unique adaptations for reproduction to rare and intriguing behaviors, the world of snake reproduction continues to surprise and amaze researchers and enthusiasts alike.
FAQ
Which Animal Gives Birth by Mouth?
While snakes do not give birth through their mouths, there are some fish species that practice mouthbrooding. Mouthbrooding is a unique form of parental care where certain fish species carry their eggs or newly hatched fry in their mouths to protect them from predators and provide a safe environment for development.
Where Does the Egg of a Snake Come Out?
In oviparous snakes, the eggs come out through the cloaca, which is a single opening used for both reproduction and waste elimination. The female snake lays the eggs in a carefully chosen location, ensuring the best chances of survival for the developing embryos.
How Do Pythons Give Birth?
Pythons are viviparous snakes, which means they give live birth. After a gestation period, which can vary depending on the species, the female python gives birth to live baby snakes. Unlike some other snake species, pythons do not lay eggs but retain the developing embryos inside their bodies until the young snakes are fully developed.
What Are the Ways Snakes Give Birth?
Snakes exhibit two main ways of giving birth: oviparous and viviparous. Oviparous snakes lay eggs, which hatch into baby snakes after an incubation period. Viviparous snakes, on the other hand, give live birth, with the young snakes being born alive and fully developed.
How Can a Snake Have Babies Without a Male?
Some snake species can reproduce without the presence of a male through a process called parthenogenesis. Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction where the female’s egg develops into an embryo without being fertilized by a male’s sperm. This phenomenon has been observed in certain snake species, allowing them to reproduce and produce offspring even without mating.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points Discussed
In this article, we have explored the fascinating world of snake reproduction, delving into the different methods by which these reptiles bring new life into the world.
Oviparous snakes lay eggs, while viviparous snakes give live birth. We debunked the myth of snakes giving birth through their mouths and highlighted their unique adaptations for reproduction.
The Importance of Understanding Snake Reproduction Accurately
Understanding snake reproduction accurately is crucial for dispelling myths and misconceptions about these remarkable creatures.
By shedding light on the true processes of snake reproduction, we can appreciate the diversity of strategies they employ for survival and the protection of their offspring.




0 Comments